As technology continues to evolve at an unprecedented rate, the future of work in Canada is being reshaped by automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics. While these advancements bring significant opportunities, they also present challenges for workers, businesses, and policymakers. In response, Canada is exploring ways to balance automation with human-centered solutions that ensure economic growth, job security, and a fair transition for all. This article examines how automation is transforming the Canadian workforce and the human-centered strategies that can guide the future of work.
1. The Rise of Automation in Canada’s Workforce
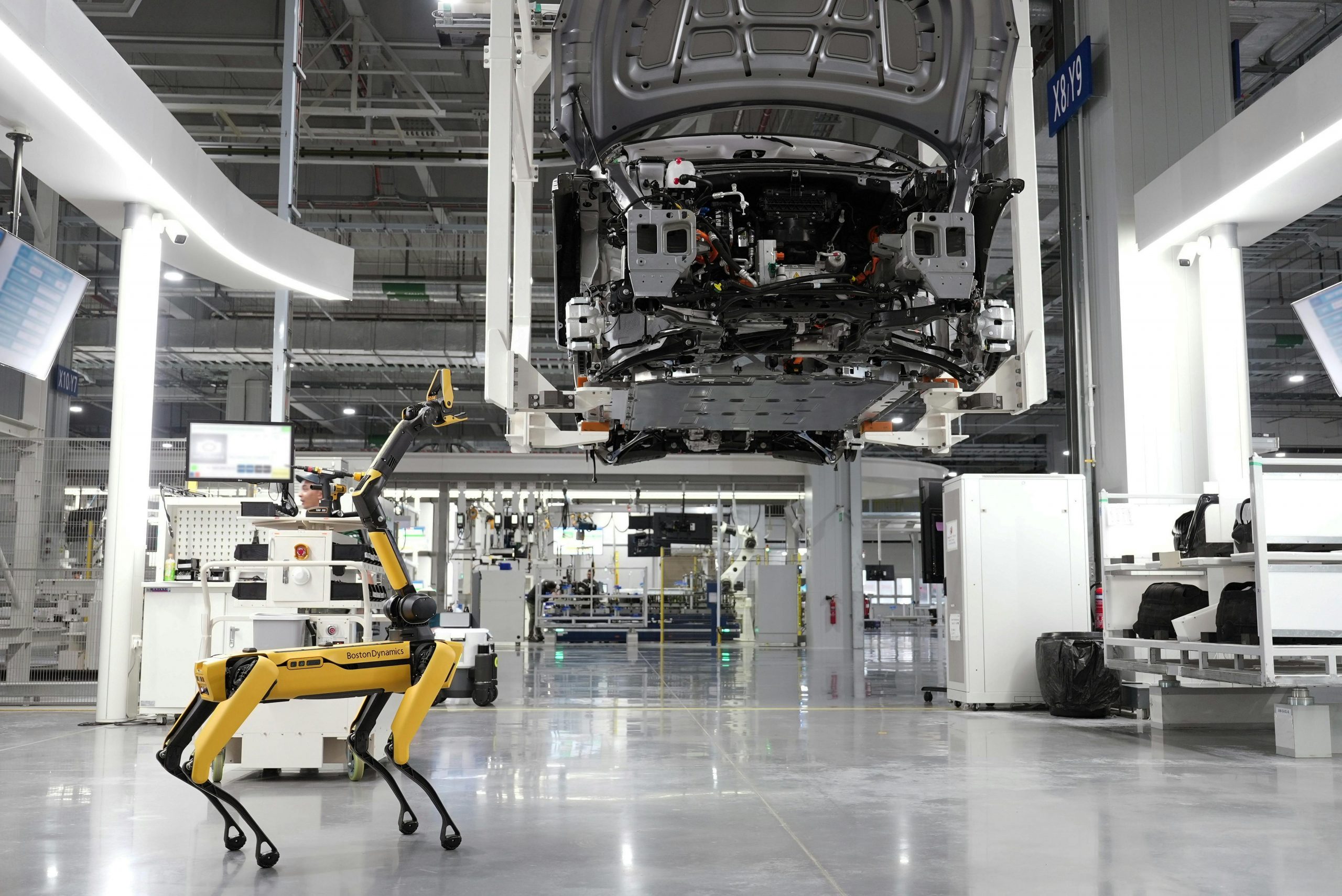
Automation has already begun to make its mark on several industries in Canada, including manufacturing, logistics, agriculture, and even the service sector. From self-checkout kiosks in retail stores to automated supply chains, the use of robots and AI technologies is increasing. Some key areas where automation is taking hold include:
- Manufacturing and Production: Automation in Canada’s manufacturing sector is boosting efficiency by replacing repetitive tasks and reducing human error. This includes the use of robots in automotive production lines and AI-driven systems for quality control.
- Transportation and Logistics: Automated vehicles, drones, and AI-powered systems are transforming how goods are transported across the country. Autonomous trucks and delivery drones are set to improve delivery speed and lower costs, although they also raise questions about the future of truck drivers and logistics workers.
- Customer Service and Retail: AI-powered chatbots and automated checkout systems are becoming common in retail and customer service settings, enhancing customer experience while reducing labor costs.
Impact for Canada’s Workforce: While automation is creating efficiencies, it is also causing disruption, particularly in sectors that rely heavily on human labor. As certain jobs become obsolete, workers will need to adapt and acquire new skills to remain competitive in the evolving job market.
2. The Challenge of Job Displacement and Reskilling
One of the most significant concerns about automation is its potential to displace jobs. In Canada, industries such as manufacturing, retail, and transportation are among the most vulnerable to automation-related job losses. To mitigate the impacts of these changes, Canada must focus on reskilling and upskilling workers to transition into new roles that are less susceptible to automation.
Key approaches to address job displacement include:
- Reskilling Programs: The Canadian government and private sector are investing in training programs aimed at helping workers develop new skills. This includes offering courses in digital literacy, AI, robotics, data analysis, and other emerging technologies.
- Support for Workers in Transition: To ease the transition, Canada is implementing programs that provide financial and career support for workers displaced by automation, ensuring they can access new job opportunities.
- Strengthening the Social Safety Net: Expanding access to benefits like unemployment insurance and creating safety nets for workers affected by automation will be crucial for managing the disruptions caused by the future of work.
Impact for Canada’s Workforce: The focus on reskilling will help reduce the negative impact of automation on employment, allowing workers to adapt to new job markets. Governments, businesses, and educational institutions will need to collaborate to provide the necessary support.
3. Human-Centered Solutions: Combining Technology with Human Creativity
While automation is making many tasks more efficient, it also highlights the importance of human capabilities that machines cannot replicate, such as creativity, empathy, and critical thinking. To ensure that automation works for people, Canada must adopt human-centered solutions that emphasize the value of human workers alongside technology.
Key human-centered approaches include:
- Collaborative Robotics (Cobots): Rather than replacing workers, collaborative robots are designed to work alongside humans, enhancing productivity without eliminating jobs. These robots can assist with physically demanding tasks, while humans focus on decision-making, problem-solving, and customer interaction.
- Focus on Meaningful Jobs: As automation takes over repetitive tasks, workers can shift their focus to more meaningful and fulfilling roles, such as roles in strategy, creativity, and leadership. The future of work will require a cultural shift that recognizes the importance of jobs that prioritize purpose and human connection.
- Promoting Employee Well-being: With the introduction of automation, there is also an opportunity to enhance employee well-being by reducing stress associated with menial tasks. As automation takes over, human workers can focus on higher-value tasks and work-life balance.
Impact for Canada’s Workforce: By placing human well-being at the center of work, Canada can build a future where technology enhances human creativity and fulfillment, leading to higher job satisfaction and economic prosperity.
4. Creating Inclusive Economic Growth through Automation
Automation has the potential to drive economic growth in Canada, but it must be inclusive to benefit all sectors and communities. To ensure that no one is left behind, policymakers must implement strategies that ensure equitable access to the benefits of automation and technology.
Key strategies to achieve inclusive growth include:
- Access to Technology for Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs): Canada’s SMEs play a crucial role in the economy, but many lack the resources to invest in automation technologies. Providing subsidies or incentives to encourage automation adoption among SMEs will help level the playing field.
- Bridging Regional Disparities: While urban centers may benefit first from automation, rural and northern communities should not be left behind. Ensuring equal access to digital infrastructure and technology will be key to creating a more balanced and inclusive workforce across the country.
- Equitable Policy Making: Policymakers must ensure that automation policies prioritize social equity, including access to reskilling programs, fair wages, and a living income for workers affected by automation.
Impact for Canada’s Economy: By ensuring that automation benefits are shared equally, Canada can foster a more inclusive economy that reduces inequality and supports workers across all sectors, regions, and backgrounds.
5. A Vision for the Future: A Hybrid Workforce
The future of work in Canada will likely be a hybrid model, where human workers collaborate with machines to achieve greater efficiency and creativity. This model will be driven by advances in AI, automation, and human-centered design.
- AI-Assisted Decision Making: In the workplace, AI will play a key role in helping workers make data-driven decisions, offering real-time insights and recommendations. This will allow employees to focus on higher-level problem-solving and strategic tasks.
- Flexibility and Remote Work: Automation will also open up new possibilities for remote and flexible work. With the rise of AI-powered communication tools, workers will be able to collaborate and work from anywhere, offering greater work-life balance.
Impact for Canada’s Workforce: The hybrid workforce will require ongoing collaboration between humans and machines. Workers will need to adapt to an evolving technological landscape, but with the right skills and mindset, they can thrive in a future where technology complements human potential.
Conclusion: Embracing a Balanced Future of Work
The future of work in Canada is one where automation and human-centered solutions can coexist, creating an economy that is both efficient and inclusive. As automation continues to transform industries, Canada’s workforce must embrace new skills, adapt to technological advancements, and focus on the human aspects of work that drive creativity and innovation. By implementing supportive policies and focusing on reskilling, inclusivity, and employee well-being, Canada can ensure that the future of work benefits everyone, paving the way for a more sustainable and prosperous future.